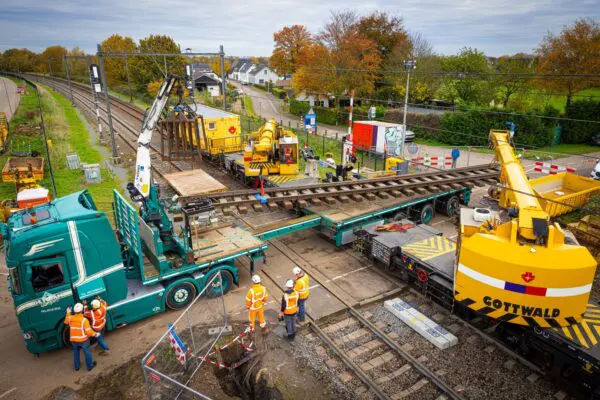
Upgrade Rail Network Rijswijk-Rotterdam

Discover the project

We are specialists in building, renewing, and upgrading rail infrastructure across all our home countries: the Netherlands, Sweden, Denmark, Belgium, and Italy. Rail construction brings together multiple disciplines — from power supply and overhead lines to signalling, track alignment, cables, and telecom. We also manage the civil works around the tracks. Every project is executed with a strong focus on safety and sustainability, using advanced machinery and the expertise of our skilled professionals.
With over 100 years of experience, we combine thorough preparation, engineering excellence, and precise execution to deliver rail projects efficiently and reliably. We hold all necessary certifications for design, engineering, construction, and maintenance of rail infrastructure.

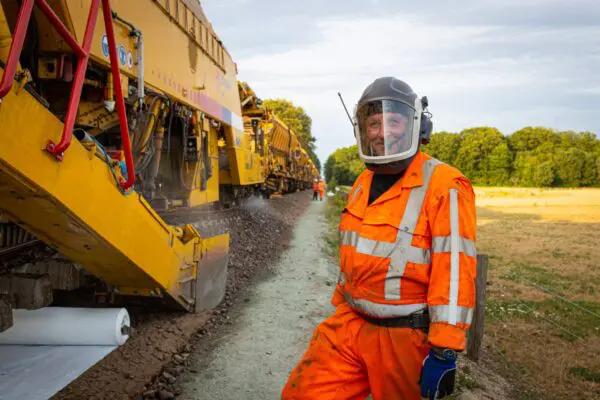
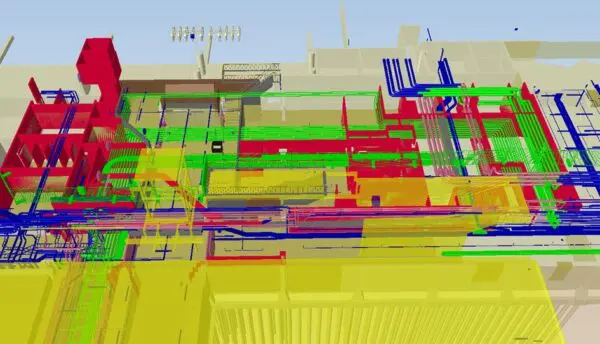
Before starting work, we map the current status of the rail network using advanced technologies such as our Leonardo inspection train, Eurailscout measurement trains, and ground radar. Both the existing and future situations are integrated into a digital model, providing full visibility of logistics, work sites, interfaces, and planning — for us and for our clients.
We continuously invest in state-of-the-art machines and collaborate with manufacturers to integrate new technologies. For repetitive tasks, we implement robotics to make our work safer, healthier, more sustainable, and more efficient.

Power Supply – Ensures energy is safely delivered at the correct voltage from the substation to the overhead line.
Overhead Line – Supplies electrical energy to trains and transfers return current to the rails. Includes supporting structures and contact wires.
Signalling – Provides train safety through electronics in relay houses and cabinets, switches, level crossing systems, and train equipment.
Track – Aligns rails, sleepers, and switches with millimetre precision and stabilises them on the ballast bed.
Cables & Pipelines – The many underground cables and pipes required for the rail system to function.
Welding – Thermite welding, ES welding. Without specialised rail welders, trains cannot run.
Surveying – Accurate measurement of tracks and surroundings before and after works.
Telecom – Installations on and around stations.
Transport & Logistics – Sustainable transport of materials and equipment to and from the rail site, often a complex logistical puzzle.




Railway construction in European urban areas faces several challenges, including limited space, strict environmental regulations and the need to manage noise and vibration in line with European rail standards. Complex public transport networks, high population density and the demand for uninterrupted urban mobility add further constraints.
The cost of constructing a new railway line in Europe depends on several key factors, including route length, local geography, environmental requirements and the complexity of the surrounding rail infrastructure. Prices can range from several million to hundreds of millions of euros, depending on whether the project involves urban environments, tunnels, bridges or upgrades to existing public transport networks.
Strukton delivers tailored railway engineering solutions and provides expert advice on cost optimisation through smart design, efficient project planning and sustainable construction techniques. By applying innovative technologies and meeting European rail standards, we help clients reduce lifecycle costs while ensuring reliable, future‑proof transport connections.
The duration of a railway construction project in Europe varies widely, depending on the project’s scale, location and the complexity of the surrounding rail infrastructure. Smaller upgrades or maintenance works may take only a few months, while major infrastructure projects — such as new rail lines, station upgrades or urban mobility improvements — can take several years to deliver due to engineering challenges, environmental requirements and European rail standards.
Strukton ensures efficient project delivery through precise planning, integrated railway engineering and smart construction methods. By coordinating with local transport authorities and applying techniques that minimise disruption for passengers and communities, we help keep Europe’s rail networks reliable, accessible and future‑ready throughout the entire construction process.
Safety is a top priority in all railway construction projects across Europe. Construction teams must comply with strict rail safety standards, European regulations and national guidelines to ensure a safe worksite and a reliable rail infrastructure. Measures typically include the use of personal protective equipment, designated worksite barriers, controlled access zones and continuous digital safety monitoring to reduce risks around active rail lines.
At Strukton, safety is embedded in our railway engineering expertise. We apply advanced monitoring technologies, rigorous training programmes and proactive risk management to safeguard our people, our partners and the travelling public. By integrating safety into every phase of a project, we help deliver secure, future‑proof rail infrastructure throughout Europe.
Railway construction involves building new rail lines, stations and other assets that expand or upgrade Europe’s rail infrastructure. This includes activities such as track installation, civil engineering works, signalling systems and the development of new corridors to support sustainable transport and growing mobility needs across European rail networks.
Railway maintenance, on the other hand, focuses on keeping existing infrastructure safe, reliable and efficient. This includes inspections, repairs, asset renewals and preventative maintenance to ensure smooth operations and compliance with European safety and performance standards.
Strukton provides both railway construction and rail maintenance services, combining advanced engineering, digital monitoring technologies and lifecycle‑based asset management. This integrated approach helps keep rail networks across Europe in optimal condition while supporting future‑proof mobility solutions.
Modern railway construction in Europe relies on high‑performance and durable materials that meet strict European rail standards for safety, sustainability and long‑term performance. Typical components include high‑grade steel rails, reinforced concrete sleepers, copper contact wires for overhead line systems and high‑quality, sustainably sourced ballast for track stability.
To support Europe’s shift towards sustainable and circular rail infrastructure, Strukton prioritises low‑maintenance, recyclable and long‑life materials. By applying circular construction principles and selecting components that minimise material consumption and maintenance needs, we help extend the lifespan of railway assets and reduce the environmental footprint of rail infrastructure projects across Europe.
In rail construction, highly specialised machinery ensures that work is carried out safely, efficiently and with minimal disruption. Typical equipment includes track‑laying trains, tamping machines, rail welding units, road‑rail excavators and ballast profiling systems, each designed to build or restore track structures with precision. These machines support both large‑scale track installation and daily maintenance operations. Innovations in automation and robotics are increasingly enhancing productivity and safety, helping infrastructure managers deliver consistent quality in a growing European rail network.
Rail construction plays a crucial role in Europe’s shift towards low‑carbon mobility. By expanding and modernising electric rail infrastructure, the sector enables cleaner transport that produces significantly lower CO₂ emissions than road or air travel. At the same time, energy‑efficient work methods—such as using low‑emission machinery, hybrid traction systems and digital tools that extend asset life—help reduce the environmental footprint of construction activities. Together, these developments strengthen a sustainable mobility network and accelerate progress towards European climate goals.